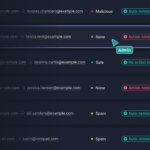
Organizations often focus their security efforts on threats from outside. But increasingly, it’s people inside the organization who cause data breaches.
There was a 47% increase in Insider Threat incidents between 2018 and 2020, including via malicious data exfiltration and accidental data loss.
And the comprehensive Verizon 2021 Data Breach Investigations Report suggests that Insiders are directly responsible for around 22% of security incidents.
So, what is an insider threat and how can organizations protect themselves from their own people?
Importantly, there are two distinct types of insider threats, and understanding different motives and methods of exfiltration is key for detection and prevention.
Types of Insider Threats
The Malicious Insider
Malicious Insiders knowingly and intentionally steal data, money, or other assets.
For example, an employee or contractor exfiltrating intellectual property, personal information, or financial information for personal gain.
What’s in it for the insider? It depends.
Financial Incentives
Data is extremely valuable.
Malicious insiders can sell customer’s information on the dark web. There’s a huge market for personal information—research suggests you can steal a person’s identity for around $1,010.
Malicious Insiders can steal leads, intellectual property, or other confidential information for their own financial gain—causing serious damage to an organization in the process.
Competitive Edge
Malicious Insiders can steal company data to get a competitive edge in a new venture. This is more common than you might think.
For example, a General Electric employee was imprisoned in 2020 for stealing thousands of proprietary files for use in a rival business.
Unsurprisingly, stealing data to gain a competitive edge is most common in competitive industries, like finance and entertainment.
The Negligent (or Unaware) Insider
Negligent Insiders are just “average” employees doing their jobs. Unfortunately, “to err is human”… which means people can—and do—make mistakes.
Sending a misdirected email
Sending an email to the wrong person is one of the most common ways a negligent insider can lose control of company data.
Indeed, the UK’s Information Commissioner’s Office reports misdirected emails as the number one cause of data breaches.
And according to Tessian platform data, organizations with over 1,000 employees send around 800 misdirected emails every year.
We’ve put together 11 Examples of Data Breaches Caused By Misdirected Emails if you want to see how bad this type of Insider Threat can get.
Phishing attacks
Last year, 66% of organizations worldwide experienced spear phishing attacks.
Like all social engineering attacks, phishing involves tricking a person into clicking a link, downloading malware, or taking some other action to compromise a company’s security.
A successful phishing attack requires an employee to fall for it. And practically any of your employees could fall for a sophisticated spear phishing attack.
Want to know more about this type of Negligent Insider threat? Read Who Are the Most Likely Targets of Spear Phishing Attacks?
Physical data loss
Whether it’s a phone, laptop, or a paper file, losing devices or hard-copy data can constitute a data breach.
Indeed, in June 2021, a member of the public top-secret British military documents in a “soggy heap” behind a bus stop.
Looking for more examples of Insider Threats (both malicious and negligent?) Check out this article: 17 Real-World Examples of Insider Threats
How can I protect against Insider Threats?
As we’ve seen, common Insider Threats are common. So why is so hard to prevent them?
Detecting and preventing Insider Threats is such a challenge because it requires full visibility over your data—including who has access to it.
This means fully mapping your company’s data, finding all entry and exit points, and identifying all the employees, contractors, and third parties who have access to it.
From there, it comes down to training, monitoring, and security.
Training
While security awareness training isn’t the only measure you need to take to improve security, it is important.
Security awareness training can help you work towards legal compliance, build threat awareness, and foster a security culture among your employees.
Looking for resources to help train your employees? Check out this blog with a shareable PDF.
Monitoring
Insider Threats can be difficult to detect because insiders normally leverage their legitimate access to data.
That’s why it’s important to monitor data for signs of potentially suspicious activity.
Telltale signs of an insider threat include:
- Large data or file transfers
- Multiple failed logins (or other unusual login activity)
- Incorrect software access requests
- Machine’s take over
- Abuse by Service Accounts
Email Security
The vast majority of data exfiltration attempts, accidental data loss incidents, and phishing attacks take place via email.
Therefore, the best action you can take to prevent insider threats is to implement an email security solution.
Tessian is a machine learning-powered email security solution that uses anomaly detection, behavioral analysis, and natural language processing to detect data loss.
How does Tessian detect and prevent Insider Threats?
- Tessian’s machine learning algorithms analyze your company’s email data. The software learns every employee’s normal communication patterns and maps their trusted email relationships — both inside and outside your organization.
- Tessian inspects the content and metadata of inbound emails for any signals suggestive of phishing—like suspicious payloads, geophysical locations, IP addresses, email clients—or data exfiltration—like anomalous attachments, content, or sending patterns.
- Once it detects a threat, Tessian alerts employees and administrators with clear, concise, contextual warnings that reinforce security awareness training