Email impersonation is a key method cybercriminals use to conduct phishing attacks. That’s because this technique is simple, accessible, and can evade many conventional security defenses.
By switching out characters in an email address, using false display names, securing top-level domains in the name of legitimate businesses, cybercriminals can impersonate your employees, vendors, or business partners — and they can do so pretty convincingly.
Looking for more background on what exactly email impersonation is? We explore the definition and different types of email impersonation in this article: What is Email Impersonation? Everything You Need to Know.
This article will guide you through how to recognize and combat email impersonation attacks.
-
Just so you know...
This article is about email impersonation, which is a phishing technique involving the creation of lookalike email addresses and false display names.
We also have guidance on defending against related cybercrimes such as email spoofing, Business Email Compromise, and CEO fraud.
Employee security awareness training
Security leaders understand how important it is to involve the whole team in a company’s cybersecurity strategy. That’s why every security-conscious organization has an employee training program that helps staff to recognize signs of a phishing attack.
But, it’s important your security awareness training is tailored, engaging, and consistently reinforced. Want more tips? Check out this article: The 7 Deadly Sins of Security Awareness Training.
And – regardless of how tailored and engaging your training is – security awareness training can’t be your only defense against social engineering — many of the more sophisticated attacks just aren’t detectable by humans.
Nonetheless, a security awareness program can help your team spot the more obvious signs of danger and understand the importance of cybersecurity.
Signs of email impersonation
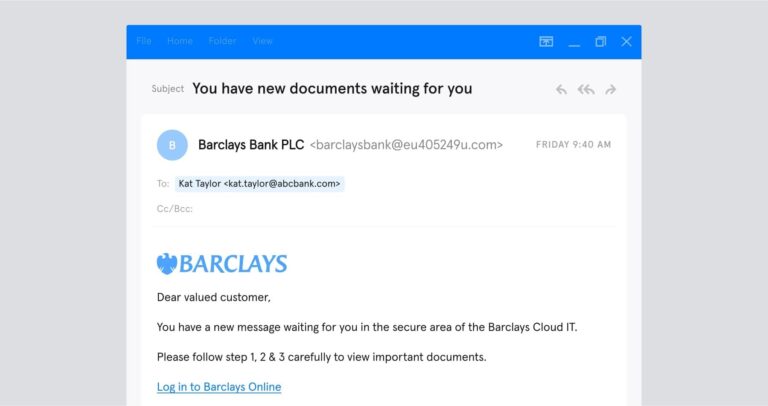
Your employees should be able to realize when something suspicious is occurring. Email impersonation can be tricky to spot, but it usually is detectable — if you’re paying attention.
So what are the signs to look out for that indicate email impersonation?
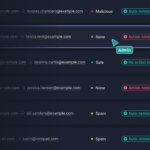
Let’s take a look at some of the different ways a cybercriminal could impersonate Elon Musk, CEO of Tesla, whose email (we’ll imagine) is elon.musk@tesla.com:
As you can see, cybercriminals have several options for impersonating an email address. Employees should look out for signs such as:
- Replacement characters (1 = l, a = 4, o = 0, etc.)
- Obscure or unexpected top-level domains
- Suspicious subdomains
- Incorrect domains associated with the username
- Display names that don’t correspond with the supposed sender
We look at these email impersonation techniques in more detail in our article What Is Email Impersonation?
Signs of a phishing attack
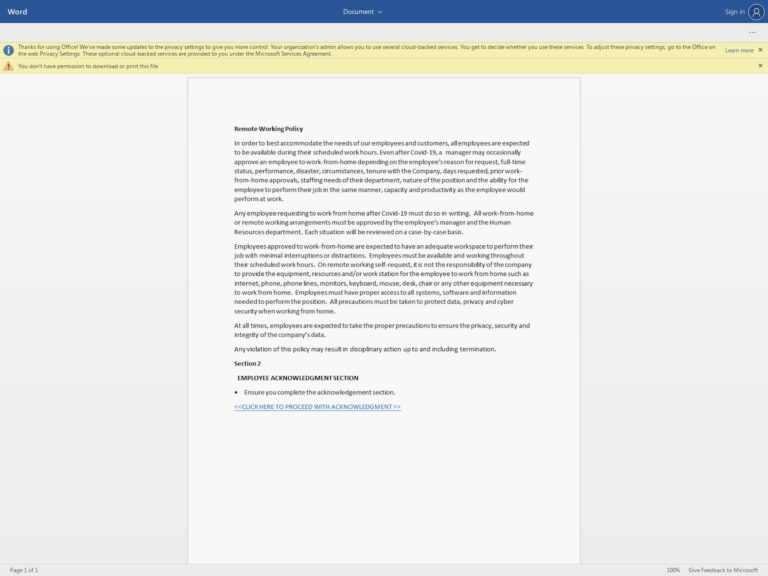
Beyond recognizing the signs of email impersonation, employees must be aware of the more general signs of a phishing attack, which include:
- A sense of urgency: Social engineering attacks depend on exploiting the target’s emotions. A phishing email will normally use a very urgent tone.
- Incorrect branding: Some phishing emails attempt to imitate a company’s logos or branding. Although this is relatively easy, amateur cybercriminals can get it wrong.
- Poor spelling or grammar: Spelling and grammar errors are normally a sign of a phishing email, particularly if the fraudster is imitating an established business.
Bear in mind that most sophisticated phishing emails don’t contain any of these giveaways. And you can’t always expect your employees to notice when they’re under threat.
We share five real-world examples of phishing attacks in this blog, which could help you educate your employees about what to look out for.
Deploy email security software
As we’ve seen, email impersonation can be challenging for humans to spot.
That’s why deploying an intelligent inbound email security solution is key to preventing email impersonation.
As your team switches to remote work, security software is more important than ever. Microsoft research shows that 80% of security professionals saw an increase in security incidents since employees started working from home.
But traditional security solutions like Secure Email Gateways (SEGs) and spam filters can’t protect your employees against many email impersonation attacks.
Tessian Defender uses machine learning, anomaly detection, behavioral analysis, and natural language processing to detect even the most subtle signs of email impersonation and phishing.
Here’s how Tessian Defender works:
- Tessian’s machine learning algorithms analyze your company’s email data. The software learns each employee’s usual communication patterns and maps their trusted email relationships — both inside and outside your organization.
- Tessian inspects both the content and metadata of inbound emails for any signals suggestive of email impersonation or other phishing attacks, such as suspicious payloads, geophysical locations, IP addresses, email clients, or sending patterns.
- Once it detects a threat, Tessian alerts employees that an email might be unsafe, explaining the threat in easy-to-understand language.
Click here to learn more about how Tessian Defender protects your team from email impersonation and other cybersecurity attacks. You can also explore our customer stories to see how they’re using Tessian Defender to protect their people on email and prevent social engineering attacks like phishing.
Not ready to learn more about the solution? That’s okay! Sign-up for our newsletter below instead. You’ll be the first to know about new research and events and get helpful checklists and how-to guides straight to your inbox.