Fact: email is responsible for up to 90% of breaches, consequently email security is at the core of keeping your organization and its data safe and secure.
As cyber risk continues to increase, having robust email threat prevention in place can mean the difference of preventing threat actors from gaining a foothold and establishing initial access. It can also provide critical visibility and control over data within the organization, significantly reducing insider risk.
Why email security deserves greater attention
It might seem like a basic question, but when you drill into what email security is and what it entails, it is fundamentally about data security. With the typical organization sending and receiving hundreds and thousands of emails on a monthly basis, explains why email is regarded as the lifeblood of organizations.
From a security standpoint, given the critical data transportation role played by email, helps explain why email security is increasingly being regarded as one of the cornerstones of data security.
Another security consideration is the open architecture character of email – making email an accessible attack vector. Anyone can send an email to any individual or organization making the threat vector extremely attractive to exploit. Want to email the CEO of a company? Their name is probably in the public domain and so their email is likely to be firstname.lastname@companyname.com or some combination thereof.
Email cyber risks are increasing
The open nature of email explains why threat actors are continuously at work in developing email-based social engineering campaigns. These campaigns are developed by using open-source information sources such as social media accounts, company PR statements and news mentions.
Recent research also points to threat actors mining dark web data dumps obtained from previous breaches for personally identifiable information (PII) to be used in impersonation campaigns.
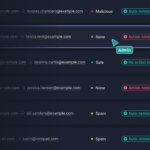
Another attack vector that is gaining prominence is credential related compromises. A credential compromise that leads to an account takeover (ATO) of a vendor in the supply chain or even an internal email account is particularly challenging to detect.
Threat actors typically leverage ATO for purposes of carrying out second stage attacks that can include email requests for invoices to be paid (invoice fraud), or delivering a malicious payload via email.
Insider threats within organizations present another threat vector on email. In fact, until the recent roll-out of behavioral-based data loss prevention (DLP), being able to detect and prevent data loss on email was near impossible.
The challenge with data loss on email is that it can occur in a multitude of seemingly innocuous ways, for example, an employee attaching the incorrect file and sending this out via email, or sending the email to the unintended recipient. More malicious acts of insider threat could include a disgruntled employee that exfiltrates sensitive company data via email, or a threat actor that has gained access via an impersonation or ATO attack.
Rule-based solutions no longer provide adequate protection
Threat actors can bypass rule-based email security controls like Secure Email Gateways (SEGs) that rely on a threat detection engine of already documented indicators of compromise. This results in effectively chancing your email security on threat detection approach of established indicators of compromise – with no protective capability against zero day attacks.
We know that threat actors don’t work this way.
Threat actors are continuously refining their attack campaigns. The result is that attack social engineering campaigns are becoming ever-more sophisticated and are increasingly able to bypass rule-based detection systems.
Some of the tried and tested methods for compromise include creating spoofed domains, leveraging compromised accounts, as well as procuring a wide-array of exploit kits on the dark web. Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS) is now sold alongside Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) on the dark web. The commercialization of these exploit kits and threat actors services are removing the barriers to entry for carrying out attacks.
On the PhaaS front, the most recent offering is the so-called Caffeine PhaaS exploit kit that enables anyone to procure the kit and launch phishing attacks against targets. The service offering includes pre-built phishing templates, available in multiple languages.
The time for advanced email protection is now
No organization can afford to neglect increasing email security risk. Only by leveraging behavioral based cybersecurity solutions will advanced email attacks be detected and prevented. This includes insider threats that leads to data loss.
Tessian’s Intelligent Cloud Email Security Platform has behavioral intelligence at its core – using Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Natural Language Understanding (NLU) – to detect advanced external and internal threats, as they manifest and in real-time. This includes threats that have been able to circumvent rule-based security controls such as SEGs.